It can also reduce maintenance costs by moving to a COTS (commercial off-the-shelf) x86-based platform while matching the reliability of a traditional RAN. COTS x86-based servers are standard and readily available computing elements from a large supplier ecosystem. Operators use them today for a range of IT needs.
“Samsung’s 5G vRAN validates a software-based alternative to vendor-specific hardware, while offering high performance, flexibility, and stability,” said Jaeho Jeon, Executive Vice President and Head of R&D, Networks Business at Samsung Electronics. “Once the solution becomes commercially available this quarter, we look forward to providing carriers with additional architectural options for building innovative and open 5G networks.”
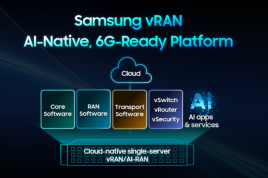
Samsung’s 5G vCU was first commercialized in April 2019 and is currently in commercial use by mobile carriers in Japan, Korea, and the United States. This new solution adds the vDU in addition to the vCU to deliver a fully-virtualized 5G vRAN. When combined with Samsung’s virtualized 4G/5G Core, the operator will be able to implement an end-to-end software-based radio and core network running on COTS servers. The company will continue to conduct vDU field trials in North America in the second half of this year.

Designed for 5G Expansion
The recent surge in broadband – especially high-quality video streaming to support work, entertainment, and learn-at-home demands—has highlighted the need for carriers to be able to quickly deploy network resources to meet the shifting requirements of businesses and consumers. Samsung’s vRAN solution, with its easy expandability and manageability, is able to support operators who want to rapidly expand network capacity and features, and evolve their networks with 5G-powered capabilities to support these demands.
“Now, more than ever, mobile operators recognize the need for quality-driven, flexible, scalable, and cost-efficient network architectures while planning for 5G network success,” said Peter Jarich, Head of GSMA Intelligence. “RAN virtualization will be an important tool in helping to deliver on those demands and Samsung’s continuing vRAN innovation positions it well to deliver.”
Samsung’s vRAN operates with or without hardware accelerators depending on factors such as total bandwidth.
Verified Performance
Samsung demonstrated its vRAN capabilities to customers in April 2020, proving the feasibility of full virtualization by operating 5G New Radio (NR) baseband functions in software running on an x86-based COTS server.
Results matched the performance of legacy hardware baseband[1]. It used Samsung’s field-proven cellular algorithms while testing Dynamic Spectrum Sharing (DSS), a technology that helps carriers take advantage of 5G in 4G frequency bands and advance a seamless evolution to next-generation communications.
Samsung Networks is a pioneer in the successful delivery of 5G end-to-end solutions ranging from chipset, radio, and core network to cloud platform for both mid-band and mmWave spectrum. The company has been supporting 5G commercial services in leading markets, including Korea, U.S., and most recently Japan, where the majority of worldwide 5G subscribers are currently located. In addition, Samsung is further expanding its global footprint rapidly to new markets from Europe to Canada and New Zealand.
[1] Based on Samsung internal testing.